Introduction:
The heart’s four valves allow blood to flow in the proper direction. Each heartbeat causes the valves to open or close. Heart valve issues can cause palpitations, chest pain, and other symptoms.
The mitral and tricuspid valves are referred to as atrioventricular valves, whereas the aortic and pulmonic valves are known as semilunar valves. Continue reading to find out more about each of the four heart valves.
What is a heart valve?
Your heart is a muscle that moves blood around your body. Heart valves are components of your heart that function as doors. They open and close to allow blood to pass from one part of the heart to another. They aid in ensuring that blood flows at the appropriate time and in the proper direction. As the valves open and close, they produce two noises that are your heartbeat.
It subsequently enters the left ventricle, also referred to as the left pumping chamber, through the mitral valve.
Finally, it passes through the aortic valve and into the aorta, where it enters the remainder of the body.

How do the heart valves function?
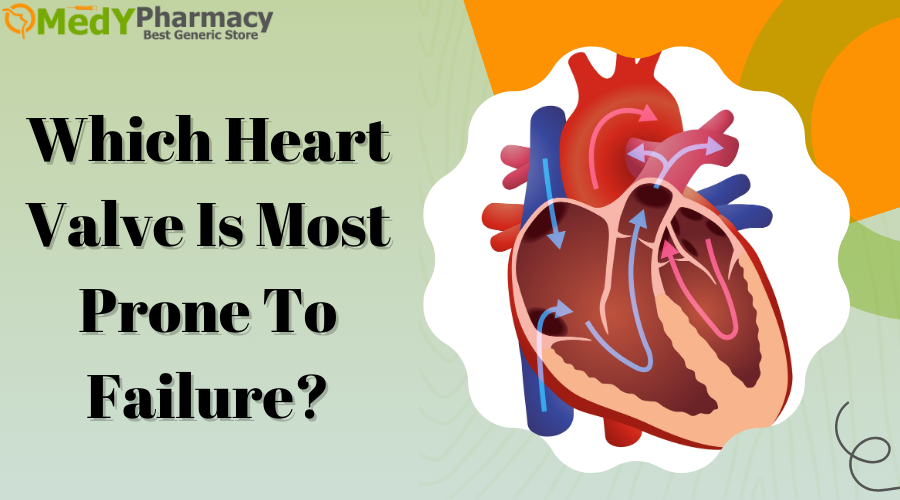
Blood flows in a regular manner through the four chambers of a healthy heart. The four chambers are the left and right atria at the top of your heart, and the left and right ventricles at the bottom. Valves, which are tiny but robust tissue flaps, connect chambers.
- Your body’s oxygen-requiring blood flows into the right atrium.
- It subsequently travels via the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
- The right ventricle pushes blood through the pulmonary valve and into your lungs, where it absorbs oxygen.
- The oxygen-rich blood then moves to the left atrium.
- The mitral valve directs blood flow into the left ventricle of the heart.
- Blood goes from the left ventricle to the rest of the body via the aortic valve.
Can heart valve problems lead to erectile dysfunction?
Endothelial dysfunction, a disorder in which blood arteries are unable to appropriately dilate (open), is one of the early stages of coronary heart disease. The penis’s blood vessels are usually the first site of erectile dysfunction. In many circumstances, ED may be the initial sign that something is wrong.
What happens if the heart valve is weakened?
Your heart’s overall functionality might not be compromised by a mild restriction. But the valve may become so narrow (stenotic) that it stresses the valve and makes it harder for you to have sex. As a result, the remainder of your body may not receive adequate blood supply.
What illnesses and disorders can harm heart valves?
- Your heart may need to pump blood more forcefully if a heart valve is not functioning correctly. Your physique will change as you mature.
- Congenital heart disease and congenital malformations in valve structure (e.g., missing or misshaped leaflets).
- Infections
- Among the underlying problems include diabetes and several cardiac diseases.
Regurgitation: Blood that flows backward due to an incorrectly closed valve is known as regurgitation. Regurgitation is also referred to as leaking heart valves. Prolapse is one particular sort of regurgitation. Prolapse is characterized by a leaflet flopping or bulging backward. It usually occurs in the mitral valve.
Stenosis: Stenosis happens when the leaflets of a valve thicken, stiffen, or stay together. Stenosis occurs when the tissue of the valve hardens, reducing blood flow. This frequently occurs when calcium and other deposits build up on the valve’s leaflets.
Atresia: Atresia refers to the absence of a valve.
The Four Heart Valves

- Aortic valve
The aortic valve is the final valve that oxygen-rich blood travels through before exiting the heart and traveling throughout the body. The valve stops blood from returning to the left ventricle.
Aortic regurgitation, also known as aortic insufficiency, occurs when the aortic valve fails to seal completely, enabling blood to flow backward.
Aortic stenosis occurs when the aortic valve thickens or hardens, restricting the channel via which blood can flow. This slows or prevents proper blood flow to the remainder of the body.
- Mitral valve
The mitral valve seals off the left atrium, allowing oxygenated blood from the lungs to flow into the left ventricle.
Mitral valve prolapse can lead to mitral valve regurgitation, which causes blood to flow backward. Mitral regurgitation can occur when the valve’s leaflets stretch apart due to a Heart attack or heart hypertrophy.
- Pulmonary valve
The next valve through which deoxygenated blood passes is the pulmonic, also known as the PH valve. It closes and opens the right ventricle, allowing blood to pass to the lungs.
Stenosis of the pulmonary valve leads it to thicken over time, limiting the opening and slowing blood flow.
Regurgitation prevents the valve from shutting completely, allowing blood to flow backward into the right ventricle.
- Tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve is named after its three flaps, which are known as cusps or leaflets. Blood exits the right atrium and goes through this valve. Blood passes from the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
Tricuspid regurgitation occurs when the valve cannot fully shut, whereas tricuspid stenosis causes the valve to thicken and narrow its opening.
What symptoms indicate a heart valve issue?
Some people may have a heart valve issue but exhibit no symptoms. Heart valve problems tend to worsen with time, thus symptoms may arise as a person ages.
Your heartbeat is produced by the opening and closing of your heart valves.
- Chest ache
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Fatigue means feeling exceedingly fatigued
- The feeling of fluttering or racing through your chest
Treatment
If a valve does not fully close, a doctor may propose surgery to fix the valve’s leaflets. Doctors choose surgery to treat mitral or tricuspid valve regurgitation.
If surgery fails to restore the valve, a surgeon may conduct a heart valve replacement. An artificial valve works in the same manner as a natural valve.
Surgery can be complicated, but a surgeon may be able to perform it using a less invasive approach.
A person may also have to treat any underlying issues. This could include taking Sugar Levels medication or modifying their pharmaceutical regimen for some illnesses, such as lupus.
How can I keep my heart healthy while I have a heart valve condition?
- Don’t smoke.
- Maintain proper blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Consume a diet high in fruits and vegetables and low in trans and saturated fats for heart health.
- Maintain a regular exercise routine.
- Make routine check-ups with your primary care physician so they can listen to your heart and catch any irregularities early.
- Antibiotics should be taken before any dental or other surgery.
- Inform all of your healthcare providers, including your dentist, that you have a heart valve problem.
Congenital
Congenital cardiac valve conditions are not always avoidable.
Some forms of heart valve illness, such as bicuspid aortic valve, are hereditary. Other occurrences are the result of cardiac abnormalities induced by diseases such as rubella during pregnancy.
Consult your doctor about steps you can take to prevent congenital heart valve disease from worsening, such as taking certain vitamins and avoiding certain infections.
How Are Heart Valve Diseases Diagnosed?
Chest X-ray – imaging that can show if you have a heart condition
EKG – a five-minute test that measures the rate and rhythm of the heartbeat and can identify if you have an irregular heart rhythm, commonly associated with a valve problem
An echocardiogram employs an ultrasound to visualize the heart and will indicate in detail if there is a heart valve problem and what type of problem it is.
Stress test – assesses the health of your heart, including pumping efficiency; several types of tests, such as an exercise stress test, may be indicated.
Cardiac catheterization puts a catheter inside the heart to examine the heart’s health and any damage

Key information on heart valve disease
Heart valve disease occurs when one or more of the heart’s valves stop working properly.
There are two major types of heart valve issues. A cardiac valve could leak (regurgitation). It may also become narrower (stenosis).
Coronary artery disease and heart attacks are two of the leading causes of heart valve disease.
Some typical symptoms include chest pain, palpitations from irregular heartbeats, tiredness, and dizziness.
An echocardiography is the most effective test for evaluating sexual health.
Medications may alleviate symptoms. A valve repair or replacement may require heart surgery.
How are heart valve illnesses managed?
Treatment for heart valve issues varies depending on your diagnosis and medical background. For the majority of patients, minimally invasive rib surgery and catheter-based techniques have replaced traditional surgery. Our cardiac specialists at the UPMC Cardiac and Vascular Institute played key roles in the early groundbreaking clinical trials that led to these advances.
What is the most effective drug for heart valve problems?
The ideal heart valve medicine addresses an underlying issue that may exacerbate your valve disorder.
If you have high blood pressure, for example, controlling it through medication and lifestyle modifications should be a focus.
Valve calcification is the accumulation of calcium on valve leaflets, which causes stenosis and significant cardiac problems.
Last Words:
If you have a heart valve condition, you should be cautious of endocarditis (heart infection). If you get symptoms of infection, such as body aches, fever, or a sore throat, contact your doctor right away.
Four valves that open and close regulate the blood flow through your heart. Age, illness, and other chronic disorders can all cause damage to the valves, and some people are born with heart valve defects.
Medypharmcy pharmacy additionally provides high-quality drugs for the treatment of intimate health disorders.