Introduction:
Within a female’s body, this hormone has other functions. If you believe that guys do not have it, you are mistaken. This hormone plays an important role in males as well.
This essay will attempt to determine the many ways in which this might impact males. We’ll look at common symptoms that people have throughout this period and try to determine some of the causes. We’ll learn more about the potential consequences of this condition, such as erectile problems in males.
The hormone that has the most impact on male sexual development and function is testosterone. However, to assist in regulating sex drive, erection capacity, and sperm generation, low estrogen, and testosterone must remain in equilibrium.
As men age, their levels of testosterone normally decline while those of estrogen rise. Except in cases when they are exceptionally high, there is no reason for alarm. This may put people at risk for diseases including diabetes and some types of cancer.
Let’s define normal and abnormal for men, discuss symptoms to look out for, and discuss what you can do about them.
Atypical sexual development may be linked to low levels at a younger age, but this is a natural aspect of ageing. If you are older than 16 and have not had your period, or if you are suffering from hot flashes, give your provider a call.
You need this sex hormone to keep your sexual and reproductive health in check. This will inevitably change during your menstrual cycle and decrease as you enter menopause. That fluctuation over time might indicate a problem that needs to be addressed by your healthcare physician.
What is Low Estrogen?
Although it has its functions, as we previously said, this hormone is typically the non-dominant one in males. The primary sex hormone in adult males, testosterone, will use the hormone to converted to estradiol.
If this happens frequently, the man would inevitably have low T levels, which might impair his libido or sex drive. It can have a variety of effects, including helping men achieve a strong erection or decreasing their sex drive. The usage of medications containing sildenafil, however, can help you avoid these issues.
Males and females both have this sex hormone, but females have more of it than males do.
This is produced by the testes, ovaries, fat cells, and adrenal glands. Women’s puberty and menstrual cycle regulation depend on it. This holds significance for the male reproductive system as well.
- The primary estrogen form
- A kind of low estrogen that is mostly generated during pregnancy
- Found in greater amounts in women who have gone through menopause
The enzyme aromatase is capable of converting testosterone into low estrogen.
- Controlling sex desire
- Getting an erection
- Creating sperm
- The function of the testicles
In the human body, this serves additional purposes as well. It can support the maintenance of heart and bone health and lower cholesterol. Mood, skin, and other bodily tissues are also impacted.
Because ovulation and the menstrual cycle depend heavily on low estrogen, this may potentially affect fertility.
A healthcare professional should be consulted for an assessment and suitable management choices, such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or other therapies, depending on the underlying reason.
What Is A Typical Male Estrogen Level?
The age and medical history of a man will determine what he needs. A physician will be able to evaluate a patient’s low estrogen levels in detail and talk about the effects appropriately.
Men have fewer amounts of this than women do, but it is still crucial for preserving general health, which includes controlling the male reproductive system, bone health, and even cardiovascular health.
- Prepubescent Male – Undetectable–16 pg/ml
- Pubescent Male – Undetectable–60 pg/ml
- Adult Male – 10–60 pg/ml
Although it is uncommon, males with this may experience hormone abnormalities or underactive endocrine function. Fertility problems or symptoms like osteoporosis may result from this.
It’s recommended for men to speak with a healthcare professional who can evaluate hormone levels and suggest suitable testing or therapies if they have symptoms or are worried about hormone imbalances.
How Does Low Estrogen Manifest Itself?
This vital hormone promotes sexual development and aids in reproductive system maintenance. It is vital to other bodily systems as well. This fluctuates throughout your life, frequently in tandem with other hormones that regulate vital bodily functions, such as your menstrual cycle. The fluctuating highs and lows that go along with this are common.
It is different when these are continuously low. If this occurs frequently, it might indicate that you are experiencing a natural transition, such as menopause. A disorder that affects your sexual development may be the cause of low estrogen, which might make getting pregnant more difficult.
Given the critical role estrogen plays in several body processes, this can show up in a variety of ways. Age, underlying medical disorders, and whether the symptoms are due to natural processes or medical problems can all affect them.
See a healthcare professional for a comprehensive assessment if you or someone you know is exhibiting signs of low estrogen. Depending on the underlying reason, they could do blood tests to measure hormone levels and recommend suitable therapies, such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or lifestyle modifications.
Factors Influencing Low Estrogen in Men
- Age
This starts to increase as the body gets ready for menstruation and sexual maturity throughout puberty. Women go through this stage when they start to develop secondary sexual traits, including breast growth and menstruation. In these modifications, this is a major factor.
Women’s production of estrogen steadily decreases as they get closer to their 40s. Because of the changing low estrogen levels, this time, called perimenopause, is marked by mood swings, hot flashes, irregular periods, and other symptoms. Unpredictable menstrual periods might result from fluctuations in low estrogen levels.
This can have an impact on a woman’s capacity to conceive since it starts to drop around this period. Pregnancy becomes challenging when the ovaries generate fewer eggs, and the ones that are produced are less sensitive to low estrogen.
- Body Fat
The ovaries cease to generate large levels of low estrogen after menopause, while adipose tissue continues to create lesser amounts through androgen aromatization. This explains why postmenopausal women with greater body fat percentages could still have estrogen levels that can be detected.
Higher low estrogen levels brought on by postmenopausal body fat can occasionally raise the chance of developing disorders like endometrial and breast cancer, which are both estrogen-sensitive malignancies. Postmenopausal women must maintain a healthy body fat percentage because of this.
Visceral fat may produce more low estrogen than fat that is stored in the hips, thighs, and buttocks. Nonetheless, a greater percentage of total body fat raises the synthesis of estrogen.
- Health conditions
When a woman’s ovaries cease releasing low estrogen before the age of forty, it’s referred to as premature menopause or POI. This can result in irregular periods, infertility, and menopausal symptoms such vaginal dryness and hot flashes.
Although the exact origin of POI is frequently unknown, autoimmune disorders, hereditary factors, and medical treatments like chemotherapy can all contribute to the condition.
Symptoms of thyroid abnormalities might overlap with those of low estrogen and include mood swings, hair loss, weight fluctuations, and exhaustion.
Ovarian damage from several cancer therapies, such as radiation and chemotherapy, can result in low estrogen levels and early ovarian failure.
Early menopause brought on by these therapies may cause vaginal dryness, hot flashes, and other menopausal symptoms.
- Medications
Compounds produced from plants that resemble low estrogen in structure and can replicate its physiological effects are known as phytoestrogens. Flaxseeds, certain herbs, and soy products (tofu, soy milk) are frequent foods that contain them.
Phytoestrogens are frequently taken into consideration for postmenopausal women’s bone health or to alleviate menopausal symptoms, even if they may have a mild estrogenic impact. They might not, however, be as effective as synthetic estrogens.
Certain herbal supplements, including red clover and black cohosh, have chemicals that may function similarly to estrogen and may help alleviate menopausal symptoms like vaginal dryness and hot flashes. But the data for their effectiveness is conflicting, and it’s unclear if they’re safe over the long run.
Who Is Most Impacted By Low Estrogen Levels?
This can affect many different types of people, but certain groups are more susceptible to the consequences of low estrogen because of particular health issues, life phases, or lifestyle choices.
Malnutrition or extreme weight loss brought on by eating disorders can result in reduced body fat, which lowers the synthesis of low estrogen. This decline is because fat cells contribute to the hormone’s production.
Osteoporosis, infertility, irregular menstruation, and other reproductive health problems might result from this. Additionally, emotional and behavioral health issues brought on by estrogen deficiency might make rehabilitation much more difficult.
The protective function of low estrogen in preserving bone strength, cardiovascular health, and vaginal/urinary tract health puts postmenopausal women at higher risk for osteoporosis, heart disease, and urinary tract infections (UTIs).
This is produced at modest levels by men and is essential for cardiovascular health, cognitive function, and bone density. Low testosterone levels are frequently the cause of low estrogen in males, although, under some circumstances, it can also happen on its own.
Erectile dysfunction, reduced libido, mood swings, bone loss, and an elevated risk of heart disease are all possible outcomes for males.
Because of their low estrogen-dependent reproductive systems, women typically suffer the most immediate and noticeable effects, but both men and women are impacted. This has a critical role in women’s mood management, heart health, bone strength, and reproductive health.
Many health problems can result from this; therefore, those who might be at risk or exhibiting symptoms must get medical advice and treatment.
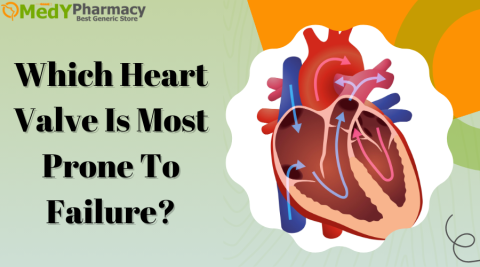
How Does low Estrogen Affect The Health Of The Male Reproductive System?
The reproductive health of men is also impacted. Sex drive, erection, and sperm production are all affected.
A low sex desire may result from this being too little. An excess of it might lead to erectile dysfunction and infertility. Breast enlargement, or gynecomastia, can result from too much estrogen.
For assistance, consult a functional medicine professional or an endocrinologist if you’re a man and worried about your low estrogen levels.
A major factor in the generation of sperm is estrogen. Sperm maturation control depends on adequate estrogen levels. Some of the testosterone is converted into estrogen by the testes’ aromatase, which also helps control the activity of the Sertoli cells, which support and feed growing sperm.
Although low estrogen plays a vital role in controlling bone metabolism, testosterone is the key hormone responsible for men’s bone health. Over time, the weakening of bones might result from an estrogen shortage.
This protects the cardiovascular system by assisting in the regulation of blood vessel health and cholesterol levels. Men who have low estrogen levels are more likely to develop heart disease and other cardiovascular problems, especially if they also have low testosterone.
How Does A Woman’s Body React To Low Estrogen?
Mainly, this affects mood control, cardiovascular health, bone health, and reproductive health. Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI), menopause, certain medical disorders, or drugs can all cause a variety of symptoms and health changes in women.
- Menstrual Cycle
This is essential for controlling the menstrual cycle. A defining feature of menopause, irregular periods, or the total cessation of menstruation, might result from a decline in low estrogen levels.
Infertility or trouble conceiving may result from ovulation not occurring due to insufficient low estrogen.
As a result, the vaginal lining may shrink, becoming less elastic and drier. Itching, discomfort, and painful sex are possible outcomes of this.
This keeps sexual function intact, and low amounts might make you less interested in having sex. Decreased sexual desire and satisfaction can also result from vaginal dryness caused by low estrogen deficiency.
- Perimenopause
Hot flashes, which are characterized by an abrupt sensation of warmth or heat and usually affect the face and upper torso, are among the most prevalent symptoms linked to low estrogen. Several times during the day or night, this might happen.
Another typical symptom of hot flashes that happens at night is night sweats, which can cause insomnia or other sleep disorders.
This affects the brain’s levels of serotonin and dopamine, which help regulate mood. Anxiety, melancholy, mood changes, and irritability can all result from a decrease in estrogen.
Increased fatigue may result from this, making it more difficult for women to maintain their energy levels throughout the day.
The hormonal changes brought on by these are believed to be the source of the brain fog or concentration issues that some women experience.
- Bone Health
Because it prevents bone resorption, this aids in maintaining bone density. Women are more vulnerable to osteoporosis and fractures when their low estrogen levels decline.
Over time, low estrogen levels can cause bone density to decrease, making bones more brittle and prone to breaking, especially in the wrists, hips, and spine.
- Cardiovascular Health
This promotes vascular health and helps maintain appropriate cholesterol levels. Women who have a drop in low estrogen levels may experience a rise in bad cholesterol (LDL) and a fall in good cholesterol (HDL), which might raise their risk of heart disease and atherosclerosis.
Additionally, this may lead to hypertension, which over time raises the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Skin and Hair
This preserves the hydration and suppleness of the skin. Women may see that their skin gets thinner, drier, and more prone to drooping and wrinkles as their estrogen levels fall.
This promotes both hair thickness and growth. Particularly around the head or temples, this may exacerbate hair loss or thinning.
Low estrogen levels cause dry, itchy skin, which many women describe, necessitating more regular moisturizing.
- Urinary Health
The urinary tract’s tissues may shrink as a result, making them more susceptible to infections. Women are more likely to have UTIs and may urinate more frequently or painfully.
The tone of the muscles around the bladder is preserved as a result. Some women may struggle to control their bladder or have urine incontinence when their low estrogen levels are decreased, especially when they laugh or sneeze.
- Cognitive Function
This contributes to the regulation of mood-affecting neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin. This may result in anxiety, sadness, irritability, and mood changes.
Long-term low estrogen levels may be linked to cognitive difficulties like memory loss and brain fog, according to some research. Postmenopausal women should be particularly concerned about this since a drop in low estrogen might impact brain function.
Lack of it might result in elevated stress and anxiety levels since it helps control the body’s reaction to stress.
- Weight Gain
The distribution of body fat is influenced by low estrogen. A decrease in estrogen causes many women to gain weight, particularly in the hips and belly. The form of the body may alter as a result.
Metabolic rate is impacted by this, and lower levels may result in a slower metabolism, which makes weight loss or maintenance more difficult.
Ways to Reduce Estrogen Levels
If a man wants to reduce his estrogen levels, he should consult his physician. Certain drugs can assist in lowering estrogen. Aromatase inhibitors and selective estrogen receptor modulators are among them.
Reducing alcohol consumption, consuming specific meals, and achieving a reasonable weight can also have an impact on hormone levels. But there isn’t enough research done in several of these fields.
Because the endocrine system is so sensitive to even little fluctuations in hormone levels, improper use of the right medications at the wrong times can have serious detrimental effects. The practice of self-diagnosis and self-treatment is strongly discouraged here.
Methods for Increasing Estrogen Levels
When a man exhibits signs of low estrogen, he should discuss treatment options with his physician.
Male hypogonadism can be treated with hormone replacement therapy. A doctor may use a patch, injection, gel, or gum-absorbing substance to provide testosterone.
Phytoestrogens are substances obtained from plants that function similarly to estrogen in the body. They may aid in naturally raising estrogen levels, although they are far less potent than the body’s natural production of the hormone.
The majority of women can safely use phytoestrogens, albeit they might not be as effective as HRT. For women seeking modest estrogen support without the use of synthetic hormones, they are particularly helpful.
Hormonal imbalances can result from excessive alcohol use since it can adversely affect the synthesis and metabolism of estrogen. Reducing alcohol use can promote normal estrogen levels.
For women who are experiencing low estrogen levels as a result of menopause, hormone treatment could be the best course of action. But there are also natural ways to promote estrogen production, including taking particular herbs or supplements, eating phytooestrogens, and leading a healthy lifestyle.
It’s crucial to speak with a healthcare professional to find the best course of action or mix of strategies for your particular circumstance. In particular, estrogen treatment necessitates weighing the advantages and disadvantages carefully; thus, consulting a healthcare provider is essential to a successful and safe outcome.
Can a Diet and Lifestyle Change Raise Estrogen Levels?
They can nevertheless be crucial for preserving a balanced hormone system and promoting the synthesis of estrogen.

- Healthy Weight
This is because a low body fat percentage might cause the body to create insufficient amounts of estrogen, which can result in irregular periods, problems with conception, and concerns related to reproductive health.
Eat a lot of fruits and vegetables, lean meats, whole grains, and healthy fats. These foods supply the nutrients required for hormone regulation, energy maintenance, and metabolic support.
Even eating too many healthful meals might cause weight gain. Avoiding overeating and promoting weight control may be achieved by being conscious of portion sizes and engaging in mindful eating.
Aim for smaller meals spaced out throughout the day to prevent hunger and the need to overeat. Eating foods high in nutrients is more important than consuming foods high in calories but low in nutrients.
- Regular Exercise
Getting regular exercise is one of the best strategies to keep your weight in check. As was previously mentioned, fat cells contribute to the synthesis of estrogen. Exercise, particularly aerobic or strength training activities, aids in muscle growth and calorie burning.
Because exercise controls the quantity of estrogen in the body, it has a balancing impact. This promotes a balanced estrogen-to-progesterone ratio, which is essential for both general and reproductive health.
The menstrual cycle can be disturbed and reproductive hormones suppressed over time by elevated cortisol levels. Frequent exercise, especially yoga, Pilates, and meditation, can help reduce cortisol levels, promote healthy estrogen levels, and assist manage stress.
- Stress Management
Establish a calming evening ritual, cut down on screen time before bed, and stick to a regular sleep schedule. Try reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to relaxing music before bed if you’re having problems falling asleep.
Don’t be afraid to ask for help when you need it, spend time with those you care about, and participate in activities that promote connection. By discussing your feelings honestly, you can keep them from intensifying and taking over your life.
Research has demonstrated that spending time outside and interacting with nature may lower cortisol levels, elevate mood, and improve brain clarity.
Regularly stroll in the park, go hiking, or just sit outside and enjoy the fresh air. Being outside for even ten to fifteen minutes might help you feel less stressed.
- Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol is processed by your liver when you consume it. The resources needed to break down hormones like estrogen are diverted to this process. An accumulation of estrogen in the body might result from liver damage caused by excessive alcohol use.
The equilibrium between estrogen and progesterone can be upset by excessive alcohol use, which may result in irregular menstrual cycles, problems with fertility, and other reproductive health concerns.
The main stress hormone produced by the body is cortisol, which alcohol can increase. Stress is linked to elevated cortisol levels, which can further upset the balance of hormones. High cortisol levels and ongoing stress might hinder the body’s production of progesterone and may make problems with estrogen dominance worse.
- Endocrine Disruptors
The body may not react to its own hormonal signals if other endocrine disruptors inhibit natural hormones from attaching to their receptors. This may lessen the hormone’s potency and interfere with regular physiological functions.
Hormone imbalances can result from some disruptors that alter the glands’ production of hormones. Long-term impacts on metabolism, growth, development, and reproduction may result from this.
Strong endocrine disruptors and dioxins can cause immune system impairment, birth abnormalities, and an elevated risk of cancer. They can also impact thyroid and estrogen hormones and disrupt hormonal signaling.
To keep the environment free of endocrine-disrupting chemicals, dispose of old electronics, insecticides, and other chemicals properly.
- Quit Smoking
One of the best things you can do for your general health, including the balance of your hormones and endocrine system, is to stop smoking. In addition to its many detrimental consequences, smoking can interfere with hormone function in several ways.
Menstrual cycles and fertility may be impacted by smoking’s effects on estrogen levels and early menopause. Cigarettes’ nicotine and other chemicals can interfere with the reproductive system and lower the synthesis of estrogen.
Lower testosterone levels from smoking can result in erectile dysfunction, decreased sperm count, and decreased libido. Nicotine can damage sperm cells’ DNA and decrease the body’s capacity to make sperm.
Smoking harms the ovaries and can lead to early menopause and unpredictable menstrual periods. Smoking can harm sperm DNA in males, which lowers fertility and raises the risk of genetic abnormalities.
Identifying High or Low Estrogen Levels
If a physician suspects that you may have either high or low estrogen levels, they will have you undergo a laboratory blood test.
In order to do this, you will need to visit a sample collection laboratory where a sample collection specialist will use a needle and vial to draw blood for analysis.
In around a week, you should have your results. You will see that this is expressed in pictograms per milliliter. Upon receiving your findings, your physician will advise you on the following steps.
There won’t be anything you need to do if they’re normal. Your doctor will suggest the following measures to help you balance your estrogen levels, though, if they are low.
How May Low Estrogen Levels Be Avoided?
The declines in estrogen that come with aging are unavoidable. Hormone balance is one of the healthy habits you may adopt to achieve overall balance in your life. Hormone treatment is not always necessary for these improvements.
For example, meditation and moderate exercise can assist with low estrogen-related tiredness and sleep issues. You may enhance all facets of your health by consuming adequate calories and the proper kind of nutrients. It is possible to increase the pleasure of sex by using a lubricant.
You could require medication to help, depending on the cause of your low levels and the intensity of your symptoms. Discuss your alternatives with your provider. If you experience difficulty becoming hard, you might utilize medications such as malegra 200.
What Amounts Of Estrogen Are Considered Normal?
This variation is typical. For example, it’s common for estrogen levels to increase during adolescence and decrease as menopause approaches. As your body gets ready for pregnancy, it’s natural for estrogen levels to increase during ovulation. When pregnancy adjustments are not required, it’s common for levels to drop during your menstrual cycle.
Your sexual life may also be impacted since reduced blood flow in the penis makes it difficult to achieve a powerful erection, necessitating the usage of tadalafil femalefil.
Levels that are regularly high or low might indicate a medical issue that needs to be addressed by your provider.
Long-term issues may result from this, or it may be a sign of an underlying illness that needs to be addressed.
If you suspect that you may have abnormal estrogen levels, you should see your doctor right away.
You may contact a local low-drug dispensary or visit a reputable online pharmacy portal such as Medypharmacy.