Introduction:
Many men struggle to acquire and keep an erection long enough to fulfill sexual engagement, which is known as erectile dysfunction. Many factors, including vascular problems or nerve injury, may be to blame. These factors may result in inflammation, the development of fibrous tissue in the penis, venous leakage, and ultimately the loss of erectile function.
Symptoms are the main emphasis of current ED therapies rather than the underlying cause. The promise of regenerative medicines, such as stem cell therapy, to treat ED, however, has experts in the area intrigued. These stem cells, which can come from bone marrow, fat, or other organs, are adaptable and can build a variety of tissues. Because stem cell therapy promotes tissue regeneration, lowers inflammation, and improves blood flow to the penis, it offers promise for treating erectile dysfunction.
Stem cell injections may help animal models regain their normal tissue shape and function. Clinical trials are now being conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of stem cell treatment in treating ED in people, albeit this is still a crucial step.
To find research on stem cell treatment for ED, a group of researchers recently searched medical databases extensively. They only covered human clinical trials; they did not include research involving animals or stem cell derivatives.
Once injected, they improve blood flow and erectile function by repairing and regenerating damaged penile tissues, blood vessels, and neurons. Overall sexual performance as well as the quality and length of erections may be significantly enhanced by this restorative process.
What is Erectile Dysfunction?
The inability to achieve or maintain an erection that is sufficiently firm for sexual activity is this. The process of erection is influenced by hormonal, psychological, and physical variables. A functional issue is not getting an erection. Although erectile dysfunction can have a variety of causes, the male hormone testosterone is the one that controls the condition.
These can include diseases including obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease, and hormone abnormalities. Additionally, lifestyle choices like smoking, binge drinking, and not exercising might have an impact.
Relationship problems, stress, worry, and depression may all affect a person’s ability to have sex. One of the negative effects of several drugs, particularly those used to treat depression, high blood pressure, or other medical issues, is erectile dysfunction.
The inability to achieve an erection may be caused by damage to the blood vessels or nerves, which may be the consequence of trauma, surgery, or diseases such as neuropathy.
A common approach to treating ED is to address the underlying cause, which may require medication, therapy, lifestyle modifications, or in certain situations, surgery. To identify the reason and choose the best course of therapy, it’s critical to speak with a healthcare professional if someone is suffering from ED.
What are Stem Cells?
In the globe, this is the most effective erectile dysfunction treatment method in terms of both treatment simplicity and unquestionably positive outcomes.
Since stem cells contact and change into the cells that give erection in the penis, they eradicate the issue of erectile dysfunction in impotence. The patient has these extracted from them by intravenous or penile injection after they are amplified in stem cell labs.
When administered initially, stem cell treatment improves ED patients by at least 50%, and with repeated doses, it produces clear improvements.
These cells are special because they can differentiate into a wide variety of body cell types. Muscle, neuron, and blood cells are only a few of the cell types into which they can divide and differentiate. They are therefore essential for tissue development, repair, and regeneration.
Their capacity to cure or aid in the regeneration of damaged tissues and organs makes them valuable in both medicine and research. For instance, stem cells are being investigated for potential use in the treatment of diseases such as cancer, spinal cord injury, and heart disease. Because they may aid researchers in understanding how illnesses originate and how to create better remedies, they are also essential to scientific investigations.
Stem Cells’ Mechanism of Action
Having trouble getting an erection for sex might be difficult. Globally, millions of men are affected. It often leads to mental distress and social problems. Among the conditions that contribute to ED include age, diabetes, heart disease, and mental health disorders.
zudena pills and other medications are helpful in this therapy. But in addition to medicine, other forms of treatment are also accessible. This involves the use of stem cells.
Other cells can be regenerated using these. This is an alternative to tadalafil femalefil for treating ED. Numerous tissues can be formed from these cells. Blood flow, nerve function, and damaged erectile tissue can all be improved by it.
Stem cells from bone marrow are often obtained as part of SCT to promote regeneration and repair. Additionally, it may be extracted from adipose tissue and administered intravenously to erectile tissue.
This keeps a pool of undifferentiated cells available for division to create new stem cells. Over time, they may maintain and repair tissues because of their capacity.
Injecting stem cells into a damaged location, for instance, allows them to proliferate constantly and provide a supply of stem cells for healing.
By promoting self-healing cells, stimulating blood vessel creation, or improving nerve recovery, this signaling may aid in tissue regeneration in ED.
Repairing injured tissues and enhancing blood flow depends on the creation of new blood vessels from preexisting ones. Because stem cells encourage the formation of new blood vessels, they can improve angiogenesis and erectile function.
Different Types of Stem Cells
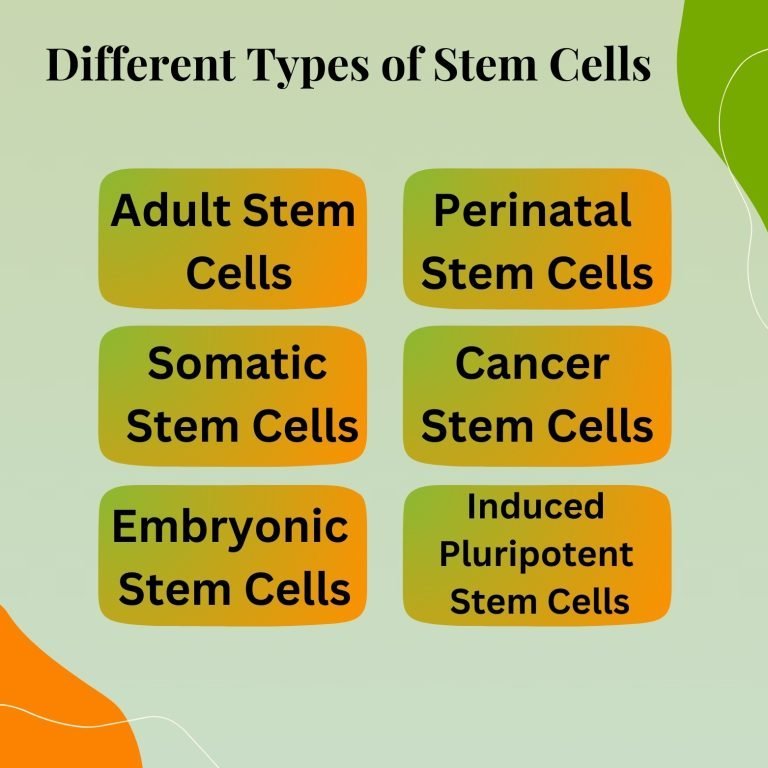
- Adult Stem Cells
Found in the brain, muscles, skin, and bone marrow, among other bodily tissues. They contribute to the upkeep and restoration of the tissue in which they live.
They can only differentiate into particular cell types associated with their original tissue while being multipotent. Hematopoietic stem cells, for instance, produce many blood cell types in the bone marrow.
A range of regenerative therapies are being investigated using adult stem cells, which are currently being employed in treatments including bone marrow.
- Perinatal Stem Cells
The placenta, umbilical cord blood, and amniotic fluid—all of which are frequently obtained before delivery—are the origins of these stem cells.
Although they can develop into many kinds of cells, they are not as adaptable as iPSCs or ESCs.
With less ethical concern than ESCs, perinatal stem cells have the potential to cure illnesses and ailments like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurological problems.
- Somatic Stem Cells
The body’s tissues include these stem cells, which are in charge of preserving and mending those tissues. Bone marrow, fat, and other tissues include mesenchymal stem cells, which may create bone, cartilage, and fat.
In the brain and spinal cord, neural stem cells can differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes.
Though not always, tissue-specific stem cells can develop into cell types unique to the tissue from which they originated.
- Cancer Stem Cells
It is believed that cancer stem cells, which are present in tumors, are what cause cancer to start and spread. Although they may self-renew and develop, they vary from typical stem cells in some ways.
Since CSCs are frequently more resistant to radiation and chemotherapy, they might develop into a variety of cell types inside the tumor, which can result in metastasis and recurrence.
Investigating ways to target CSCs for more potent cancer therapies is still ongoing.
- Embryonic Stem Cells
These are derived from embryos, usually at an early developmental stage called the blastocyst. The most adaptable kind of stem cell, they can develop into every kind of cell found in the body.
The promise of ESCs in drug testing, disease modeling, and regenerative medicine is enormous. Their extraction necessitates the killing of embryos, which makes their usage morally dubious.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
By using genetic factors to reprogram adult somatic cells back into a pluripotent state, iPSCs are produced.
Similar to ESCs but not produced from embryos, pluripotent cells do not raise ethical issues.
IPSCs have promise as a tool for drug testing, disease modeling, and possible treatments. They can be applied differently for each patient to prevent immunological rejection. Their complete potential in regenerative medicine is still being investigated.
Other than Stem Cell Therapy In What Ways Does Fildena 100 Help?
For some patients, stem cell treatment may be costly. It is appropriate to use Fildena or Fildena 150 in place of this treatment. It promotes blood flow, which keeps the erection strong throughout intercourse. This eliminates the possibility of cell rejection as well.
Sildenafil makes breathing easier and lessens PAH symptoms by relaxing and enlarging the lungs’ blood veins, which improves blood flow and lessens the strain on the heart.
A disorder known as Raynaud’s phenomenon occurs when smaller arteries, usually found in the fingers and toes, constrict in reaction to stress or cold, resulting in decreased blood flow and color changes.
In people with Raynaud’s disease, sildenafil may be used off-label to assist increase blood flow; however, this is not a frequent application and needs physician supervision.
Despite not being FDA-approved for females, some evidence indicates that sildenafil may be helpful for women with sexual arousal issues, especially those who have inadequate vaginal blood flow. Sexual enjoyment may be enhanced by increasing blood flow to the clitoris and other genital tissues.
Using Stem Cells to Treat ED
The mainstay of stem cell treatment for erectile dysfunction is mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which may be obtained from a variety of sources, including bone marrow and adipose tissue. The ability of these MSCs to develop into other cell types, including smooth muscle and endothelial cells, is essential for the structural stability and functionality of erectile tissue.
MSCs are beneficial for treating erectile dysfunction in several ways. They can control the inflammatory response, which is frequently linked to erectile dysfunction, enhance blood flow by encouraging the development of new blood vessels, and encourage tissue regeneration and repair.
Furthermore, in the context of erectile dysfunction treatment, additional stem cell types, such as adipose-derived stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells, could potentially contribute to vascular health and tissue regeneration.
Low testosterone levels might occasionally be linked to erectile dysfunction. This may be employed to improve testicular function or increase testosterone production, therefore addressing hormonal imbalances that lead to erectile dysfunction.
ASCs are derived from adipose tissue and are a form of mesenchymal stem cell. Because of their regenerative properties, they may be injected straight into the penis to improve blood flow, stimulate nerve regeneration, and aid in tissue restoration.
Treatments for ED using stem cells are still in their infancy. There is still a dearth of long-term safety evidence, despite some encouraging findings from modest human trials and animal research. Thorough research is required to determine the possibility of problems, such as tumor growth or undesired differentiation.
For ED, this is now mostly accessible through clinical trials or specialty clinics that provide experimental therapies. Although the first findings are promising, further investigation is necessary to ascertain the long-term advantages and hazards of stem cell therapies for erectile dysfunction.
Potential of Stem Cell for Erectile Dysfunction
In recent years, stem cell treatment has garnered a lot of attention due to its extremely promising potential for treating ED, especially in those whose ED is brought on by poor blood circulation, nerve damage, or tissue damage. Since much of the research is still in the preclinical or early clinical stages, the discipline is still in its infancy.
- Angiogenesis
Poor blood flow to the penis is a major cause of erectile dysfunction (ED). This can be caused by vascular injury or blood vessel constriction from diabetes or atherosclerosis.
Angiogenesis, or the creation of new blood vessels, may be accelerated by stem cells, which would increase blood supply to the erectile tissue. The blood supply required for an erection may be restored by stem cells encouraging the development of new vessels in the penis.
- Nerve Regeneration
Prostate surgery, spinal cord injuries, and diseases like diabetes can all cause nerve damage that can disrupt the signals required to have an erection.
Damaged nerves may be repaired or regenerated by neural stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which may be converted into nerve cells. Nerve function, which is essential for achieving and sustaining an erection, may be restored by this procedure.
Additionally, this can generate growth factors that promote the survival of already-existing nerve cells and aid in the repair of injured nerve fibers.
- Hormonal Function
In certain instances, hormonal abnormalities or low testosterone levels may be connected to ED. By encouraging the activity of the testes or even prompting the synthesis of testosterone, stem cells may aid in the return of normal hormone levels.
With potential advantages for both sexual performance and general well-being, stem cell treatment may provide men with ED associated with hypogonadism (low testosterone production) an option.
- Treatment of Vascular ED
This may help treat vascular erectile dysfunction, which is caused by damaged or restricted penile blood vessels, since they may repair endothelial cells and encourage angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels.
This may increase erection initiation and maintenance as well as the penis’s vascular health.
- Personalized Medicine
Its individualized approach is among the most intriguing features of stem cell treatment for ED. Stem cells can be obtained from the patient’s own body, reducing the possibility of immunological rejection. Based on each person’s requirements and underlying reasons, this method could provide a customized treatment for ED.
The creation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from the patient’s own skin or blood cells, for example, might further customize the treatment and lower the risk of immunological rejection-related problems.
- Damaged Penile Tissue
Stem cell treatment is beneficial for ED brought on by tissue damage, whether from age, trauma, diabetes, or other causes. Endothelial cells in the penis and smooth muscle cells are among the tissues that stem cells may replenish.
For instance, multipotent stem cells called mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) have been researched for their capacity to repair injured erectile tissue and enhance function. These stem cells can fix fibrosis, which is a common cause of ED and can develop after an injury.
- Improving Sexual Function
One of the main reasons for ED is diabetes, which also frequently results in vascular damage, nerve damage, and poor tissue regeneration. Through nerve regeneration, blood flow enhancement, and erectile tissue restoration, stem cell treatment may be able to address several reasons for erectile dysfunction in diabetic individuals.
Stem cells can treat ED symptoms and increase sexual function, according to studies on diabetic animal models; nevertheless, further human clinical trials are required.
What Is The Stem Cell Therapy’s Mechanism Of Curing ED?
These cells are prepared and injected straight into a man’s penis, which contains erectile tissue, based on NIH results. ED can be cured more quickly with the targeted injection. After injection, these stem cells begin to regenerate. Once they begin to regenerate, the injured neurons and blood cells are repaired.
Injecting stem cells into the injured penile tissue allows them to develop into the particular cell types that need repair. To fix injured tissue, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) or adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) can develop into smooth muscle and endothelial cells.
By encouraging the development of new blood vessels, the growth factors released by the stem cells also aid in tissue regeneration and enhance blood flow.
By restoring the penis’ structural integrity, this regeneration enhances its capacity to respond to sexual excitement.
Because stem cells secrete factors that control fibroblasts, the cells that produce collagen and scar tissue, they assist prevent the creation of fibrotic tissue.
By decreasing the quantity of scar tissue in the penis and encouraging the regeneration of healthy erectile tissue, this can enhance tissue flexibility and function.
The stem cells start differentiating into the necessary tissue types, repairing blood arteries, promoting neuronal function, and regenerating damaged cells. As the tissue heals and grows back, individuals could eventually start to experience better erectile function.
Given its capacity to heal injured tissue, enhance blood flow, restore nerve damage, and lessen fibrosis, stem cell treatment for ED has enormous potential. Nevertheless, more investigation and clinical testing are required to completely grasp its potential, create standardized treatment plans, and guarantee its efficacy and safety in the management of erectile dysfunction.
What Role May Stem Cells Play In Treating Erectile Dysfunction?
The ability of stem cells to regenerate has long been recognized. Since their potential was discovered, researchers and medical professionals from a wide range of fields have attempted to employ the cells for various purposes.
In urology, and more especially erectile dysfunction, these effects are probably brought about by the release of growth factors and cytokines into the bloodstream, maybe in addition to their migration to the main pelvic ganglia and cellular differentiation.
These can promote the healing of penile tissues, as well as the nearby blood vessels and nerves. While neither palliative nor symptomatic, this may have long-term therapeutic effects. Accordingly, stem cells may help prevent erectile dysfunction (ED) or repair sexual function that has been damaged. However, stem cells are not as helpful as medications like Viagra.
Damage to the nerves can also cause ED by impairing one’s capacity to get or keep an erection. To improve erectile function, stem cells may help regenerate nerve cells, which might improve brain-penis communication.
Conventional ED therapies, including drugs or penile implants, may need invasive procedures or have negative side effects. Although they are still in the experimental stage, stem cell-based treatments might provide a less intrusive, more natural alternative with fewer long-term adverse effects if they work.
Although early clinical trials and animal models have demonstrated some promising results, stem cell therapy for ED is not yet a commonly used or FDA-approved medication. Although the study is still in its early phases before stem cell therapies for ED can become a commonplace choice, issues about safety, effectiveness, and long-term impacts must be resolved.
In conclusion, stem cells may present a viable treatment option for erectile dysfunction, especially in cases where traditional medicines fail. However, much more study is needed to ascertain the safety and efficacy of these treatments.
Drug Composition for ED
To manage ED, many medications are available. Here, a medication such as Super P Force is typical. The qualities of Cialis are present in these. This promotes blood flow. Additionally, it makes a man’s nerves in that area larger. These are now popular therapies for male erectile dysfunction.
TRT can help men with ED who have low testosterone levels by bringing their hormone levels back to normal. Low testosterone can lead to decreased erectile function and libido.
In certain instances, psychological conditions like anxiety or depression are the root cause of ED. By treating the psychological underpinnings of these disorders, medications like SSRIs may enhance sexual function. On the other hand, SSRIs themselves occasionally cause ED as a side effect.
To encourage tissue regeneration and restore damaged penile tissues, novel therapies including gene therapy and stem cell therapy are now in the experimental stage. Despite their potential, these treatments have not yet received FDA approval for general use.
PDE5 inhibitors, the most popular medication for ED, work well for the majority of ED-afflicted men. Because the effectiveness of various medications might vary depending on specific conditions, it is always best to see a healthcare expert to determine the best course of action.
How Does an Erectile Dysfunction Treatment Using Stem Cells Look?
In the urological sector, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are by far the most often employed cell types, and direct injection is the most widely used technique for delivering stem cells for the treatment of ED.
Usually, it takes several applications over a few months to see any benefits. The course of therapy can potentially be repeated every few years if needed.
The stem cells are separated and concentrated in a laboratory after the tissue or bone marrow is removed. The objective is to optimize the therapeutic impact by obtaining a high concentration of healthy stem cells.
After that, a direct injection of the concentrated stem cells is made into the corpus cavernous, which is the penile tissue. The injections can occasionally be used in conjunction with other regeneration treatments, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP), to increase their efficacy.
This can aid in the regeneration of injured erectile tissue by encouraging the production of new cells and the healing of damaged smooth muscle and blood vessels. The penis’s capacity to get and sustain an erection may be enhanced by this.
Stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction has a bright future, particularly for men who have not responded to conventional therapies like injections or oral drugs. More patients may find stem cell treatments to be a feasible alternative to existing medications as research advances, offering a potentially more natural, long-lasting cure with fewer side effects.
Although it is still in its infancy, stem cell therapy for ED is not yet a recognized or accepted treatment. However, for patients with underlying tissue or vascular damage, the regeneration potential of stem cells holds out hope for a novel ED treatment strategy. Future therapies could be more broadly accessible, safe, and successful thanks to further research and clinical trials.
How Are Stem Cells Prepared?

- Source Selection
A crucial component of stem cell research and treatment is the source selection of stem cells, as the kind of stem cell selected can have a big impact on its potential, applicability, and ethical issues.
While iPSCs provide an option that circumvents these limitations, embryonic stem cells present serious ethical questions.
In conclusion, the ideal source of stem cells is determined by the particular use, moral issues, and difficulties associated with manipulating and using the stem cell type.
- Harvesting
Stem cell harvesting is the process of obtaining stem cells from a particular source for use in treatment or research. The harvesting techniques differ according to the stem cells’ origin.
To maintain ethical and legal compliance, the harvesting procedure is strictly controlled, and gaining informed permission is crucial, particularly for human-derived cells.
For medication testing and the research of genetic abnormalities, harvested stem cells—particularly iPSCs—are utilized to develop disease models.
- Processing
Stem cell processing encompasses the methods and approaches utilized to separate, refine, cultivate, and get stem cells ready for study or medical usage. This stage is essential because it guarantees that the stem cells are healthy, free of contaminants, and in the right condition for their intended application.
The main elements of stem cell processing are summarized here, along with the procedures, difficulties, and technologies employed.
Growth factors and cytokines that support the particular differentiation route of adult stem cells are frequently present in the culture media.
- Purification
A crucial first step in getting stem cells ready for study, clinical usage, or medicinal application is purification. To ensure that the finished product is devoid of contaminants, undesirable developed cells, and other non-stem cell populations, purification aims to separate the particular population of stem cells from a diverse mixture of cell types. The safety, effectiveness, and consistency of stem cell treatments are improved by purification.
- Expansion
When more stem cells are cultivated while retaining their undifferentiated condition and desirable characteristics, this is referred to as stem cell expansion. To get enough cells for clinical usage, research, or therapeutic applications, this step is crucial.
With some cells developing and others remaining undifferentiated, stem cell cultures can occasionally become heterogeneous during growth. Maintaining the population’s homogeneity is crucial to making sure the enlarged cells continue to be appropriate for their intended use.
- Quality Control
To guarantee that stem cell populations are safe, viable, and functional for use in research or clinical settings, quality control, or QC, is an essential stage in the stem cell processing workflow. Quality control procedures aid in the identification of any contamination, genetic anomalies, or loss of stem cell characteristics that can jeopardize the results of treatment or study.
The quality control procedure uses a mix of molecular, biological, and functional tests to make sure stem cells fulfill the requirements for research or clinical usage.
To verify the stem cell’s ability to differentiate into the intended lineage, differentiation experiments are conducted. This can be accomplished by subjecting the cells to certain differentiation agents and evaluating the expression of the differentiated lineage’s genes and protein markers.
- Administration
Stem cell administration is the procedure of giving stem cells to a patient or study model to treat them. Making sure the stem cells go to the right place in the body, integrate correctly, and carry out their planned tasks depends on this stage. The kind of stem cells, the ailment being treated, and the delivery system that optimizes therapeutic effectiveness and reduces dangers all influence the administration technique.
Patients are given genetically engineered stem cells as part of several cutting-edge therapy strategies. Before the stem cells are transplanted or given to the patient, they must be edited to fix genetic flaws or improve their capacity for regeneration.
How Much Do These Drugs Need to Be Taken?
A tablet such as Vidalista 60 mg one pill should be taken half an hour before engaging in sexual activity. This will support the maintenance of an erection during intercourse. It is not recommended to consume more than one pill at once. Since it improves blood flow, taking too many pills might have the opposite effect. Two pills can be taken by a male in two days.
- Excessive dosage
A medication overdose can be detrimental to one’s health. If more than is required, blood pressure might rise quickly. If it makes breathing difficult, you should see a doctor right away. Being cautious to avoid consuming too much is suggested. Any medication that has the properties of Tadalafil might be hazardous if used in excess.
- Dose Miss
No negative effects will occur if a person skips one dosage of these medications. However, it will assist a guy overcome ED if he takes one pill daily. The effects of taking these medications may last a lifetime.
Evaluation of ED Pills
Reviews from men who have used these medications are positive. Men reported improvements within a week of using these medications, according to Medypharmacy. But each man’s reaction to the medication is unique. But usually speaking, using these medications for a month helps treat ED.
The medications may take up to 30 minutes to start working. Taking a medication such as Tadarise around half an hour before having intercourse is recommended.
The procedure of stem cell treatment takes longer. In addition, it is costly. Medicines are affordable and convenient to have. Nevertheless, each has advantages and disadvantages.
The aforementioned discussion suggests that ED can be cured by stem cell treatment. Medications are another choice. It is significantly simpler to obtain medications.
Despite its effectiveness, stem cell treatment can be costly. However, the body does not suffer any negative effects from stem cell treatment. The same person receives the cells and has them injected. Therefore, the body is not required to take in any foreign substances.