Introduction:
Both men and women often experience hunger just after sexual activity. It might result from a hormonal shift your body is going through or physical tiredness that causes hunger.
This post will explain the causes of post-sex hunger and even provide advice on how to eat to prevent overindulging in unhealthy foods. If, on the other hand, you suffer from erectile dysfunction, perhaps it’s time to start taking sildenafil.
Since your body needs food to function, it’s common to experience hunger after going several hours without eating. However, something may be wrong with your health if your stomach grows even after eating.
Polyphagia is the term used in medicine to describe severe hunger. See your doctor if you are constantly hungry.
It alerts you to the need to replenish and eat when your energy levels are low. The type of food consumed, its effect on blood sugar, and the rate at which it is broken down by the body all influence how frequently people experience hunger.
After having sex, it’s rather common to go directly to your kitchen. Your body must eat to recover from the physical strain and replenish the energy that was expended during the activity.
What Is Hungry After Sex?
The term “hungry after sex” describes the extreme physical hunger that some people feel after engaging in sexual activity. This post-coital hunger can be explained by the biochemical and emotional reactions that occur in the body during and after sexual activity.
Sex raises body temperature, raises heart rate, and burns calories, making it a type of physical effort that is frequently compared to a mild to moderate workout.
The body may react to this activity by craving nutrition to refuel energy stores, particularly in those with rapid metabolisms or those who have not eaten in a long time.
In addition to the physical exertion, sex causes the production of several chemicals that can activate the brain’s reward and pleasure regions, such as serotonin, oxytocin, and dopamine. Following these chemical spikes, the body may enter a more relaxed state when hunger and other fundamental needs are more apparent.
The chemicals oxytocin and prolactin, which are linked to bonding and satisfaction, may also help refocus attention from the intensity of intimacy to more basic requirements like rest and nourishment. Some people find that eating after sex is a reassuring routine that helps them relax or increase their level of closeness.
After Having Sex, Is Feeling Hungry Normal?
This is extremely typical for many people and is natural. Many physiological changes occur in your body during sexual activity—your heart rate rises, blood flow increases, calories are used, and many muscles are activated, much as during a mild workout.
Naturally, this physical activity might make you hungry, especially if you haven’t eaten recently or if you have a particularly high metabolism.
Beyond the physical aspect, however, sex also raises levels of dopamine, oxytocin, serotonin, and even adrenaline, which are all involved in mood, arousal, and relaxation.
Following an orgasm, the body frequently settles into a relaxed state when the elevated feelings subside and you become more conscious of your fundamental needs, such as hunger, thirst, and sleep. Prolactin, which is connected to sexual fulfilment, can also add to that mellow feeling after sex, and when the body relaxes, hunger often kicks in as a way to regain homeostasis.
A comfortable ritual between lovers, eating after sex, may also be an emotional or bonding event for some people. After intimacy, if you find yourself desiring a snack, don’t panic; it’s simply your body requesting a little replenishment after all that effort.
Hunger Can Be Caused By Several Reasons
- Diabetes
A chronic illness called diabetes affects how your body uses blood sugar, which is your primary energy source. Insulin is a pancreatic hormone that normally facilitates the entry of glucose from meals into your cells for energy. This procedure isn’t functioning correctly in people with diabetes.
Diabetes can cause hyperglycemia, or elevated blood sugar, which over time can harm organs and result in consequences such as heart disease, nerve damage, renal failure, eye issues, and more if it is not properly treated.
To manage the illness and avoid complications, it is essential to keep an eye on blood sugar levels and adhere to a treatment plan. Despite the seriousness of diabetes, people with the disease can live active, fulfilling lives if they receive the right care.
- Blood Sugar
Blood sugar, sometimes referred to as blood glucose, is the quantity of glucose in your blood. Glucose is produced by your digestive system after meals and subsequently enters your circulation.
Hyperglycemia is the term for when blood sugar levels are excessively high. It can cause symptoms like thirst, exhaustion, and frequent urination, as well as more significant health problems, including heart disease, nerve damage, or eyesight loss over time.
Hypoglycemia is a condition in which blood sugar is excessively low. It can result in shakiness, disorientation, lightheadedness, and, in extreme situations, unconsciousness.
It is normal for your blood sugar levels to rise after meals and fall during fasting or in between meals. Blood sugar levels that are persistently high or low, however, may be troublesome.
- Sleep
A biologically necessary and natural process, sleep enables your body and mind to relax, heal, and rejuvenate. From memory and immunological response to mood management and metabolism, it is essential for almost every facet of physical and mental well-being.
A whole sleep cycle, which repeats many times during the night, lasts around 90 minutes, with each stage serving distinct restorative purposes.
7-9 hours of good sleep per night is advised for the majority of individuals. Generally speaking, kids and teens require more. Serious health effects of chronic sleep deprivation or poor sleep quality include diminished immunity, emotional disorders including anxiety and depression, reduced cognitive performance, and an increased risk of obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure.
- Stress
Stress is your body’s normal reaction to any physical, emotional, or mental demands, difficulties, or imagined threats. In moderation, stress may be a motivating factor that keeps you attentive and focused during crises or critical activities. Acute stress is what this is, and it usually passes as soon as the issue is rectified. On the other hand, chronic stress—that is, stress that lasts for weeks, months, or more—can seriously harm your health.
Stress triggers the release of chemicals like cortisol and adrenaline when your body goes into “fight or flight” mode. These hormones speed up your heartbeat, stiffen your muscles, and increase your attention, preparing your body to handle danger.
Numerous things can cause stress, including pressure from the workplace, money troubles, relationship troubles, significant life changes, or even internal concerns and expectations. Individual differences exist in how we respond to stress, and developing effective coping mechanisms is essential for mental and physical health.
- Diet
A person’s regular food and drink choices are referred to as their diet, and they are fundamental to their general health and well-being. A balanced diet gives your body the vital nutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water—that it needs to function correctly. Not only should you eat to feel satisfied, but you should also feed your body in a way that promotes your immune system, long-term illness prevention, energy levels, and cognitive function.
Depending on their age, gender, amount of exercise, health, cultural preferences, and personal objectives, various people have varying nutritional demands.
A person with diabetes, for instance, could concentrate on controlling carbohydrate intake and meal timing to maintain stable blood sugar levels, whereas an athlete might prioritise protein and complex carbohydrates to support both performance and recuperation.
Having a healthy connection with food, paying attention to your body’s signals of hunger and fullness, and engaging in mindful eating are all ways to lead a healthier lifestyle. A well-considered, adaptable diet may help you achieve your goals, whether they be to feel better, increase muscle, reduce weight, or manage a medical condition.
- Medication
The term “medication” describes drugs used to treat, control, or avoid illnesses, diseases, or ailments. A doctor may prescribe medication, it may be purchased over the counter, or it may be used as part of complementary therapies. They might be tablets, liquids, creams, injections, or inhalers, and their main function is to help control symptoms, treat illnesses, or support chronic diseases.
Generally speaking, generic medications are less costly than name-brand ones and have the same active components, potencies, and dose forms. Because they are less expensive and equally effective, generic medications are frequently chosen.
- Pregnancy
The body of a pregnant woman changes in several ways during her pregnancy. The placenta’s growth, the uterus’s expansion, and the increased blood volume are all made possible by hormonal changes that support the pregnancy. In addition to these changes, women may also go through emotional and mood swings, which are frequently brought on by hormonal and physical changes in the body.
Prenatal care is essential for the whole pregnancy. Frequent visits to the doctor enable the tracking of the pregnancy’s development, guaranteeing the health of the mother and unborn child. This might involve screening for specific disorders like pre-eclampsia or gestational diabetes, as well as blood tests and ultrasounds.
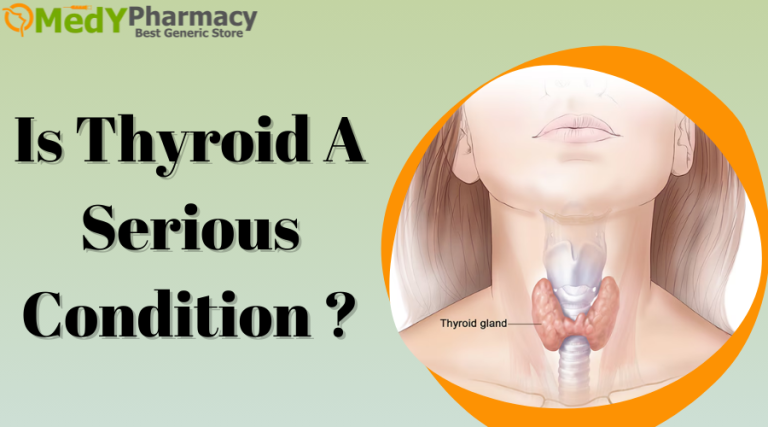
- Thyroid
A neck lump, trouble swallowing, hoarseness, or neck or throat discomfort are some of the symptoms. Family history and genetic variations can raise the risk, while the precise explanation is unclear.
When treating thyroid cancer, radioactive iodine therapy and hormone replacement therapy are usually administered after the thyroid is surgically removed (thyroidectomy).
- Dehydration
A lack of water and electrolytes required for regular physiological processes results from dehydration, which happens when your body loses more fluids than it takes in.
Water accounts for over 60% of your body weight and is essential for functions including digestion, temperature control, joint lubrication, and nutrient transfer. Your body doesn’t work as well when you’re dehydrated, which can cause a variety of physical and emotional problems.
Dehydration can be severe and harmful or moderate and treatable. Maintaining awareness of your fluid intake is crucial, particularly during times of increased activity, sickness, or hot weather.
- Exercise
It can include everything from regular activities like walking, gardening, or dancing to more scheduled routines like jogging or weightlifting. Maintaining excellent health and avoiding a variety of physical and mental health problems requires regular exercise.
Exercises that improve balance and coordination are particularly important as we age. They include activities like tai chi, balance drills, and exercises that focus on core stability. These exercises help prevent falls and improve overall functional movement.
An Increase in the Hormones That Cause Hunger
Your body experiences a major hormonal shift during intercourse. You feel more enjoyable, driven, and fun after having sex. This sensation is typically brought on by an increase in hormones like oxytocin and adrenaline, which cause excitation, according to studies.
The latter is a kind of hormone that, once you arrive, makes you feel content and joyful. Some studies indicate that an increase in these hormones may make you feel hungrier. A physician may prescribe medications such as tadafem if you are unable to fall asleep quickly.
Having Sex While Distracted, Even If You Haven’t Eaten
You feel good after having sex, and your sexual fantasies frequently take you away. Your mood is normally centred on obtaining pleasure and satisfaction when you are feeling hungry.
You may thus not feel hungry until you sate your inner sex urges, even if you haven’t eaten anything before intercourse. When you finish the deed, though, your brain immediately becomes hungry. You may get Cenforce 200 wholesale, which provides you with a hard erection rapidly, so don’t worry if you don’t get hard with it.
Most individuals think that having sex is a way to feel satisfied. Your body wants to reward you after you have finished having sex because it is filled with sensations of pleasure and fulfilment. And what better way to sate your taste senses than by snacking on your favourite snacks?
But having anxiety or being in a foul mood cannot make you feel as excited during sex. It might be difficult for men as well to achieve a firm erection. Get rid of these problems quickly by taking a fildena double 200 mg right now.
Do Women Typically Feel Hungry After Having Sex?
Many women experience hunger after intercourse. It is a component of their sex. Some women frequently experience hunger after having sex with their boyfriend. The reason for this is the increased energy levels that occur during sexual engagement. During sexual activity, women’s bodies restore nutrients and trigger desires.
You should thus consume light foods like yoghurt or a piece of fruit, a sandwich, or soup after sex, depending on your body’s needs. It is advised to have a few wholesome items that will help you feel more energised and perform better after having sex.
After-sex hunger can be influenced by blood sugar changes in women with certain medical illnesses, such as diabetes or polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). In order to replenish blood sugar levels following physical activity, the body may send out hunger signals.
A greater appetite after sexual activity is not uncommon for some women; however, not all of them will experience this. Numerous variables, including energy consumption, hormone changes, metabolism, and even psychological reactions, may be to blame for this. Each person’s body is different, and factors such as food, mental condition, and general health might affect how hungry they feel after having sex.
Is It Typical For Men To Feel Hungry After Having Sex?
It is common for men to get hungrier after having sex. Feeling hungry after sex is a common occurrence for males. It’s due to this high level of physical exertion, like having sex. In addition to raising their appetite for food and fuel, it speeds up their metabolism. You should consume some snacks to help you recuperate from your sexual encounter. It aids in reducing hunger and reviving your energy.

- Energy Expenditure
Physical movement, including heartbeats and muscular contractions, is a part of sexual activity. It eats up energy and burns calories, even if it might not be as strenuous as other types of exercise. Some men may therefore experience an increase in hunger as a result, since the body indicates a need for replenishment to restore energy levels.
- Hormonal Changes
Numerous chemicals, including dopamine, endorphins, and oxytocin, are released by the body during intercourse and can impact mood and bodily experiences. These hormones affect appetite and satiety as well. Following sexual intercourse, some people may experience increased hunger due to the release of these hormones.
- Blood Circulation
A brief rise in metabolism can result from sexual activity because it raises heart rate and blood flow. The body may react to this elevated metabolic rate by making you feel hungry as a way to get more nutrients.
- Psychological Factors
The sensation that follows intercourse can occasionally be both psychological and physiological. For example, following an enjoyable and private encounter, some people can feel the need to overindulge or turn to food for solace.
- General Hunger
The fact that hunger may just be a normal physiological reaction to any physical activity or exertion should also be taken into account. After sex, a person may experience hunger similar to that experienced after exercising or engaging in any physically taxing activity if they haven’t eaten in a long time or if their appetite is generally greater.
Some men sense hunger after sex, while this is not universal and may be a normal aspect of the body’s recuperation and energy balance. It might be worthwhile to investigate lifestyle factors like nutrition, exercise habits, or stress levels if the hunger is excessive or appears out of the ordinary.
Does Eating A Meal Before Having Sex Make Sense?
It is undoubtedly a good idea to eat before engaging in sexual activity. For what reason? The rationale is that if you eat a good meal and some energy-boosting foods, you will have more stamina when you stay in bed, which might help you live longer.
- Low libido
- Physical burnout
- Lack of energy
When combined, these disorders may lead to difficulties with male erection. However, recovery is feasible with the use of Vidalista tablets.
What Foods Are Appropriate to Eat After Having Intercourse?
Let’s now discover what kinds of foods may be consumed to sate your appetite following intercourse.
- Consume carbohydrates to assist you in regaining your lost energy and recovering from fatigue.
- Consume additional vitamins because your muscular tissues are depleted of them due to metabolism.
- Considering how much internal protein your muscles lose, consume protein.
When you eat, drink some water since you can be thirsty or mildly dehydrated from not drinking for a long period.
Erectile dysfunction, for which Vidalista 40 mg is required, can also be prevented with a nutritious snack or supper.
Want Some Junk Food After Having Sex?
Once more, the body’s need for “comfort food” is linked to the propensity for junk food after sex. When it comes to this element of men’s health, you are not alone, so don’t worry.
Instead of avoiding foods high in protein after the act, couples typically turned to junk food like pizza and fries. Men experiencing distress and battling with erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation are also likely to have this type of yearning.

- Energy Depletion
Sex uses energy and burns calories, particularly if it’s vigorous or physically demanding. After that, the body naturally seeks food to replenish its energy stores. Junk food’s high calorie count frequently makes it alluring since it’s a quick and filling way to get your energy back.
- Hormonal Responses
Your body releases several chemicals during intercourse, including endorphins, oxytocin, and dopamine. As part of that post-pleasure feeling, cravings for cosy, decadent meals may surface while the body is still experiencing increased relaxation and fulfilment.
- Psychological Satisfaction
In the perceptions of many, food and pleasure are frequently linked. Comfort foods, such as chips, chocolate, or pizza, are linked to pleasure and emotional comfort; therefore, many individuals may have cravings for them after a fulfilling sexual encounter. Eating “junk food”-style meals might seem like a method to increase that moment of enjoyment or to reward oneself even more.
- Serotonin Boost
Serotonin is released during sex, which might make you feel good. After that, you may naturally want to eat something fun and cosy, like your favourite junk food, to keep feeling good.
- Relaxation and Stress
Many people report feeling more relaxed and less stressed after having sex. The body can be hankering after easy, fast energy sources to maintain that calm mood. Junk food, which is frequently high in fat and sugar, can cause the brain to react in a joyful way, which will make the closeness you just had even more relaxing.
- Social and Cultural
Occasionally, it’s only a cultural association or habit. Indulging in food may be a treat, and some individuals may feel that it’s OK to indulge after a private encounter. Sharing junk food is often thought of as a way to strengthen bonds, whether it’s after a relaxing date night.
Is It Bad to Eat Unhealthy Snacks After Having Intercourse?
It’s okay to occasionally consume junk food after sex as long as you’re maintaining an active lifestyle and eating a balanced diet. An attitude to food that is well-rounded and healthful can include occasional self-indulgence.
After physical activity (such as sex), eating heavy, oily, or highly processed food may cause digestion to slow down a little. The act of having sex itself raises your heart rate and increases blood flow, but afterwards, your body may be more focused on relaxing, and your digestive system may slow down. A large or high-fat snack may cause you to feel bloated, lethargic, or even uneasy.
It’s crucial to recognise any patterns when eating turns into a coping strategy for feelings like stress, boredom, or even post-sex relaxation, even if this isn’t always a bad thing. If this becomes a regular habit, it can be worthwhile to consider if it stems from an emotional desire as opposed to a physical need.
Is Your Hunger Increased by Sex?
There are both scientific and psychological reasons why this may make some individuals feel hungrier. Although not everyone experiences increased hunger after sex, it’s a rather common and understandable feeling for those who do.
The sensation of relaxation and contentment that permeates your body and mind can occasionally trigger appetites for other pleasurable things, such as food. Food may trigger hunger even if you weren’t previously famished if it’s already connected to comfort, reward, or bonding.
Timing, emotional state, hormone responses, and physical intensity all affect the outcome. Although not everyone will experience this reaction, if you frequently discover that your appetite increases after sex, it’s probably your body’s natural attempt to find balance and fulfilment.
This might indicate that you need to eat more. But it can also be brought on by certain dietary and lifestyle choices, such as eating a diet poor in nutrients, eating too fast, and experiencing stress.
If you frequently feel hungry, consider evaluating your food and lifestyle to see if there are any adjustments you can make to feel fuller.
If you must take Vilitra 60 tablets for erectile dysfunction, it is recommended to get them from an online pharmacy such as Medypharmacy at the best price.