Introduction:
Coughing is a natural physiological reaction that shields our respiratory system from harm. Expelling irritants, mucus, or other objects that could obstruct our airways is a reflex. Persistent coughing, however, raises concerns about its nature and possible link to more serious illnesses such as chest infections.
If you cough, do you have an infection in your chest? We will examine the many causes of coughs and the connection between coughs and chest infections in this thorough investigation into the complex world of coughs.
This is not produced by an ineffective or dry cough. A dry cough may be caused by a tickling feeling in the throat. Following a cold, flu, or COVID-19 infection, dry coughing may occur. Chronic dry coughs can be brought on by GERD, heart failure, and lung cancer, among other illnesses. You can also feel a dry cough and discomfort in your chest.
What is a chest infection?
An illness that affects the lower portion of your respiratory tract is called a chest infection. You have bronchi, lungs, and windpipe in your lower respiratory tract.
The two most prevalent forms of these are pneumonia and bronchitis. Mild to severe chest infections are possible.
An illness that affects both your lungs and the bronchi, the lower big airways, is called a chest infection. The most frequent illnesses of the chest are bronchitis and pneumonia. Between 1% and 10% of bronchitis instances are caused by bacteria, while most cases are caused by viral infections. Most often, a bacterial infection causes pneumonia.
This cannot be officially diagnosed by a doctor. A respiratory system infection is typically meant when someone says they have a chest infection. The airways and lungs comprise your respiratory system.
The Various Aspects of Coughs
The complex process of coughing is impacted by numerous variables. It may be brought on by smoking, allergies, pollution, infections, or underlying respiratory disorders.
Coughing occasionally might not be a big deal, but a chronic or persistent cough could indicate a problem that needs to be addressed.
If you have a cough that lasts longer than two weeks, you should consult a doctor. The underlying cause of the cough may be treated with medicine, lifestyle modifications, or a mix of the two.
Vidalista black 80 mg is a potent way to improve the quality of your erection and boost your sexual performance, so use it to elevate your private times.
When I Cough, Why Does My Chest Hurt?
Coughing up air is the essence of an ineffective dry cough. If you have a dry cough that is strong or lasts more than three weeks (chronic cough), you may be straining your chest muscles or lungs. With the cough, you might get chest pain.
Most people who cough dryly experience a tightening in their chest. You might experience pressure, as if a weight were resting on your chest, or a squeezing sensation.
Unexpected, sudden chest pain may indicate a heart attack. You ought to get medical attention right away.
How Can A Tight Chest And Dry Cough Be Treated?
When you address the root problem, the majority of dry coughs go away. Cough medications that are sold over the counter are typically not very effective. Additionally, cough medications should not be given to children under the age of four due to the possibility of severe adverse effects.
- Remain Hydrated By Consuming A Lot Of Drinks.
If your airways are irritated, try hot tea or water with lemon and honey.
- Cough Drops Or Hard Candies Can Be Sucked.
When a firm lozenge is sucked, saliva is produced, which helps to clear the throat. However, avoid giving cough pills or hard sweets to kids younger than four. They can choke.
- Take A Honey Tablespoon.
Most over-the-counter cough medications don’t work as well as honey, according to studies. Based on the age of the patient, your healthcare expert can advise on the appropriate quantity of honey. Don’t provide honey to a youngster younger than one year. Honey can give newborns botulism.
- Put A Humidifier To Use.
With a cool-mist humidifier, moisture is introduced into the air. Dry coughs are lessened by this additional moisture, which also relieves sore throats and nasal passages. Another way to increase your moisture intake is to take a hot bath or steamy shower.
How Can I Avoid Having A Tight Chest And A Dry Cough?
Steer clear of chemicals, mold, and odors that might cause irritation and allergies.
To avoid respiratory diseases, wash your hands often and maintain proper hygiene.
Avoid secondhand smoke and give up smoking.
Treatment for a Chest Infection
If a virus is the cause of your chest illness, antibiotics won’t work. Rather, your therapy will concentrate on reducing your symptoms until you start to feel better.
Antibiotics will be used to treat any bacterial infections you may have. These can be taken as tablets at home in moderate cases.
You might need to receive intravenous antibiotic treatment in a hospital if you have a serious bacterial chest infection.
Antibiotics are ineffective in treating acute bronchitis since the majority of cases are caused by viral infections.
When taking antibiotics, you are nearly as likely to have adverse effects like diarrhea and vomiting as to benefit from the medication.
The more often mild diseases are treated with antibiotics, the more likely it is that the bacteria will become resistant to them and cause more serious infections.
Generally speaking, these are only advised if it is believed that you are at a higher risk of contracting pneumonia or another secondary lung infection because of things like:
- Prolonged lung or heart issues, such as heart failure or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Being immunocompromised, or having an impaired immune system, brought on by a disease like diabetes or cancer, or by specific medical treatments like chemotherapy
Natural Treatments for a Chest Infection
The symptoms of your chest infection might be lessened by using these natural cures.
- Reduce your temperature and ease any aches and pains by taking over-the-counter drugs such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil).
- Make coughing easier by using over-the-counter expectorants or decongestants to help break up mucus.
- Get as much sleep as you can.
- Be sure to stay hydrated. This can help you cough up more easily by releasing mucus and keeping you hydrated.
- When you sleep, avoid lying flat. This may result in the accumulation of mucus in your chest. To raise your head and chest at night, use additional pillows.
- To ease coughing, use a humidifier or breathe in steam vapor.
- If you coughed too much and your throat hurts, have a warm drink of honey and lemon.
- Avoid using cough suppression medications. Coughing aids in the removal of mucus from your lungs, which helps you recover from your infection.
Investigated Causes of Coughs
Dissecting the several elements that can cause coughs is crucial to understanding their complexity. Common viral infections, like the flu or the common cold, are well-known for causing coughing as the body tries to get rid of the invasive bacteria.
An ongoing cough can also be brought on by smoking, bacterial infections, allergies, and environmental contaminants. Furthermore, persistent coughing may be a symptom of underlying respiratory disorders like asthma or COPD.
Additionally, coughing may be a side effect of some drugs or a reaction to stress and worry. Zudena 100 mg tablet is a powerful remedy for sexual energy that will give you a long and pleasurable erection.
- Differentiating Infections of the Chest
Infections of the chest, often known as lower respiratory tract infections, cause inflammation of the lung tissue and airways. Bacteria like Streptococcus pneumonia and viruses like influenza can cause these diseases. Chest infections can include fever, coughing, chest discomfort, dyspnea, and the production of bloody or colored mucus.
Usually, medications, rest, and lots of fluids are used to treat chest infections. In extreme situations, hospitalization can be required. Long-lasting erections can be achieved and maintained with the help of tadalafil femalefil.
- Getting Around the Cough Chronicles
The most important question that many people wonder is if a cough always indicates a chest infection. Even though chest infections frequently cause coughs, not all coughs are a sign of these illnesses. When determining whether a cough is normal or indicative of a more serious respiratory condition, the length and accompanying symptoms are crucial.
If you have a chronic cough along with other symptoms like fever, exhaustion, and shortness of breath, it’s serious and needs to be treated by a doctor. Usually, a cough that goes away after two weeks is not a cause for concern. sildigra 250mg guarantees a long-lasting and fulfilling erection while maximizing sexual performance.
- Interpreting Severe and Prolonged Coughs
It’s critical to comprehend the temporal characteristics of coughing. Less than three-week-long acute coughs are frequently viral and result from illnesses like the flu. Persistent coughs that have lasted for longer than eight
Weeks may indicate the presence of underlying medical conditions including chronic bronchitis, GERD, or asthma. Crucially, chest infections, particularly bacterial ones, can prolong a cough.
Additionally, chest infections might result in more severe side effects including pneumonia, which needs to be diagnosed and treated very away. Enjoy the satisfaction of a strong erection with Manforce tablet, a reliable option for men looking to improve their closeness.
A Chest Infection: What Causes It?
Either a viral or bacterial infection can induce a chest infection. Depending on the illness type, the precise reason will vary.
For instance, a virus frequently causes bronchitis, but bacteria are the primary cause of the majority of pneumonia cases.
When someone with an infection coughs or sneezes, respiratory droplets are released into the air, which might infect you with a chest infection. This is because the illness is carried by respiratory droplets.
The infection can also spread by touching your lips or face after coming into contact with a surface that has the virus or bacteria on it.
When an infected individual coughs or sneezes, these illnesses are typically transferred. This sends microscopic fluid droplets that contain the bacterium or virus into the atmosphere for other people to breathe in.
Also, if you cough or sneeze onto your hand, an object, or a surface and someone else shakes your hand or contacts those surfaces before touching their mouth or nose, they may contract the infection.
- Infants and early children
- Youngsters who struggle with development
- Senior citizens who are extremely overweight
- Ladies who are pregnant
- Those who smoke
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis, diabetes, kidney disease, asthma, heart disease, and other long-term illnesses
- those with compromised immune systems, which may be brought on by recent sickness, transplants, high-dose steroids, chemotherapy, or other medical conditions such as an undetected HIV infection.
Types of a Chest Infection
The 3 primary forms of chest infections are pneumonia and acute bronchitis.
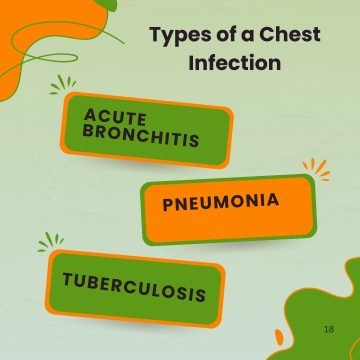
- Acute bronchitis
An infection of the bronchi causes inflammation, which is known as bronchitis. Inflammation is known medically as “itis.” It may be acute or persistent. Acute refers to a brief duration, whereas chronic refers to an extended duration.
The most prevalent cause of acute bronchitis is a viral infection. Germ (bacteria) infection is a less frequent cause. To learn more, refer to the Acute Bronchitis booklet.
- Pneumonia
This can be a dangerous bacterial chest infection, which is typically a lung infection. Usually, antibiotic treatment is required. For further information, see the accompanying pamphlet titled Pneumonia.
An infection known as pneumonia affects the lungs’ airways, resulting in inflammation and swelling of the air sacs with pus or fluid. Although pneumonia can be caused by a variety of pathogens, the most frequent ones are bacterial and viral.
A person who is ill may cough, sneeze, or exhale particles into the air, which could cause them to proliferate in the airways of others. This could result in pneumonia.
- Tuberculosis
A bacterial infection called tuberculosis arises in the lungs or airways as a result of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
In the US, tuberculosis is uncommon. According to the American Lung Association, contracting tuberculosis is not simple.
However, TB can be dangerous or even lethal if left untreated. The majority of TB cases end without sequelae if a patient gets timely, efficient medical care.
Recovery time from chest infections
Even though they can be painful and inconvenient, chest infections usually go away on their own without medical intervention. In most cases, symptoms go away in a few days.
Coughing and mucus production are common after the virus has cleared up for many people.
But according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), acute bronchitis symptoms usually go away in less than three weeks. See a doctor if your symptoms persist for more than three weeks.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Sometimes a chest infection, like acute bronchitis, will clear up on its own without the need for medical attention.
A pharmacist can help by suggesting over-the-counter (OTC) decongestant drugs to help clear your chest of any mucus, which will facilitate coughing.
- Are older than 60-65
- Are expecting a child under five who has chest infection symptoms
- Have a chronic illness or a compromised immune system and cough up blood or mucus that is bloody.
- Suffer from worsening symptoms like a headache or fever.
- Feel lightheaded, disoriented, or confused; experience rapid breathing, chest pain, or shortness of breath.
To make a diagnosis, the physician will assess your symptoms and conduct a physical examination, which includes listening to your heart and lungs as you breathe using a stethoscope.
To find out where and how severe your illness is, the doctor could take an X-ray of your chest.
Additionally, they could draw blood or sputum to determine the source of your infection. These tests can also assist them in determining which medication to take if bacteria are the cause of your chest infection.
Symptoms: The Investigative Process for Chest Infection Diagnosis
The concomitant symptoms are crucial in determining whether a cough is related to a chest infection. A chest infection usually manifests as a series of symptoms, such as fever, chest discomfort, dyspnea, and the creation of thick or discolored mucus.
It is crucial to get evaluated by a doctor when these symptoms coexist with a cough to make an accurate diagnosis and take prompt action. Chest infections can cause severe side effects like bronchitis or pneumonia if they are not treated. The sildenafil citrates in Cenforce 200 provide a strong, long-lasting erection for remarkable, unforgettable intimacy.
- The Odyssey of Diagnostics
A diagnostic process is initiated by medical personnel in response to persistent coughs and probable chest infections. Finding the underlying reason requires the use of blood tests, sputum cultures, chest X-rays, and physical examinations.
In order to assess lung health and determine whether any underlying respiratory diseases are aggravating the cough, respiratory function tests may also be used. To look into the reason for the cough further, a CT scan might be required in certain situations.
In certain situations, the diagnosis may need the use of a bronchoscope. Fildena Tablet is a state-of-the-art remedy for erectile dysfunction that will help you achieve your sexual goals and boost your confidence.
- Methods of Therapy
The underlying reason determines the best course of treatment for chest infections and coughing. The main goal of managing viral infections is to reduce symptoms with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter drugs.
On the other hand, antibiotics are frequently required for bacterial chest infections. It is essential to finish the recommended antibiotic course to stop the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Other therapies for chest infections, like inhalers, decongestants, and chest physical therapy, may be necessary in certain situations. In extreme situations, hospitalization can be required.
General Symptoms of a Cough
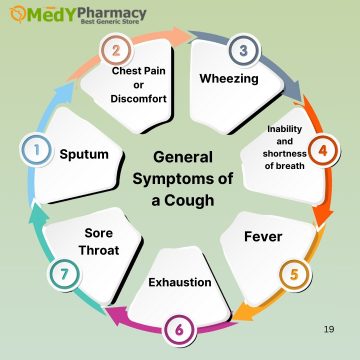
- Sputum
Green, white, or clear sputum: Frequently observed in bacterial diseases such as pneumonia or bronchitis or viral infections such as the common cold.
A bacterial infection is frequently indicated by yellow or green sputum, but viral infections can also exhibit this symptom as they worsen.
A more serious illness such as tuberculosis, lung cancer, or severe bacterial pneumonia may be indicated by blood in the sputum.
- Chest Pain or Discomfort
Some people who cough frequently have chest pain or soreness. “Cough-induced chest pain” is a common term for this type of pain, which can be sharp or painful.
Muscle soreness: The diaphragm and surrounding muscles may be strained by frequent coughing.
- Wheezing
A high-pitched whistling sound that is frequently produced during exhalation in diseases like pneumonia, bronchitis, and asthma.
- Inability and shortness of breath
This may occur when lung function is impacted by the underlying illness or when coughing is intense. It is prevalent in bronchitis, pneumonia, and asthma.
- Fever
When an infection is the cause of a cough, a low-grade to severe fever may accompany it.
- Exhaustion
The body uses energy to cough, thus prolonged or intense coughing can lead to fatigue.
- Sore Throat
Coughing too much or too harshly might cause inflammation or irritation in the throat.
How Do Chest Infections and Coughs Connect?
A chest infection may be indicated if a cough lasts for an extended period or is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, dyspnea, or chest pain. The body may cough due to the irritation and inflammation in the lungs or airways, which can be caused by a bacterial or viral illness.
Most infections, such as pneumonia or acute bronchitis, cause severe inflammation of the lung tissue or airways, which results in a chronic cough. The body may create thick mucus or pus that is coughed up if the chest infection is bacterial.
What is the diagnosis process for chest infections?
In addition to examining you, your doctor will inquire about your symptoms. Typically, they will listen to your chest during the physical examination.
- Tests on blood
- An examination of your phlegm to determine the infection’s source
- To determine the source of the illness, a chest x-ray and a swab of your throat or nasal
How a chest infection can be avoided
Make sure your hands are clean, especially before touching your lips or face or eating.
Consume a balanced, healthful diet. By doing this, you may strengthen your defenses against illness.
Get a vaccination. An infection like influenza, for which there is a seasonal vaccine, can lead to chest infections. To prevent yourself from pneumonia, you might also want to think about getting the pneumococcal vaccine.
If you’re already sick, wash your hands often and protect your mouth when you sneeze or cough. Get rid of any used tissues the right way.
- Hand hygiene
Frequent hand washing aids in stopping the spread of illness.
- Vaccination
Pneumococcal and flu vaccines, among others, can help prevent some kinds of chest infections.
- Avoid exposure
Especially if your risk is high.
When Should You Get Medical Assistance?
You should visit a doctor if you have a chronic cough and any of the following symptoms:
- Fever that is either persistent or extremely high.
- Breathlessness or shortness of breath.
- Acute or excruciating chest discomfort.
- Coughing out mucous that is stained with blood.
- Excessive weakness or exhaustion that impairs your functioning.
- Deterioration of cold or flu symptoms.
If you have a chest infection such as pneumonia or bronchitis, or if your cough is caused by something else, a medical practitioner can assess your symptoms, perhaps with a physical examination, chest X-ray, blood tests, or sputum culture.
Preventing Respiratory Issues: Constructing Strongholds
Taking a proactive stance is necessary to avoid chest infections and the coughing they cause. Respiratory infections can be prevented by maintaining good respiratory hygiene, which includes frequent hand washing and following coughing protocol.
Vaccination against certain illnesses, such as the flu and pneumonia vaccines, and avoiding close contact with sick people offer extra protection against certain infections. Enhance your sexual performance with Sildigra 250mg Tablets, a revolutionary product for enhancing the quality of erections.
It is not always the case that a cough indicates a chest illness. Determining if medical treatment is necessary requires an understanding of the complexities of coughs, their duration, and any accompanying symptoms.
Seeking medical attention is advised if a chronic cough is accompanied by fever, chest pain, or trouble breathing. By promoting general respiratory health and lowering the risk of chest infections and related coughs, preventative interventions like immunisations and proper respiratory hygiene help people breathe easier.
Come in-store and talk to one of our Medypharmacy representatives for more guidance on how to manage a cough or chest infection; they can help you choose the best course of action.